LAN vs WAN: Which One Is Best For Your Business?
LAN vs WAN: two terms that are frequently used when discussing computer networks. In the realm of networking, understanding the differences between Local Area Networks (LANs) and Wide Area Networks (WANs) is crucial.
In this article, I will discuss the key distinctions between LAN vs WAN, examining their functionalities, advantages, and use cases. So let’s dive in and explore the world of LAN vs WAN!
What is a LAN?
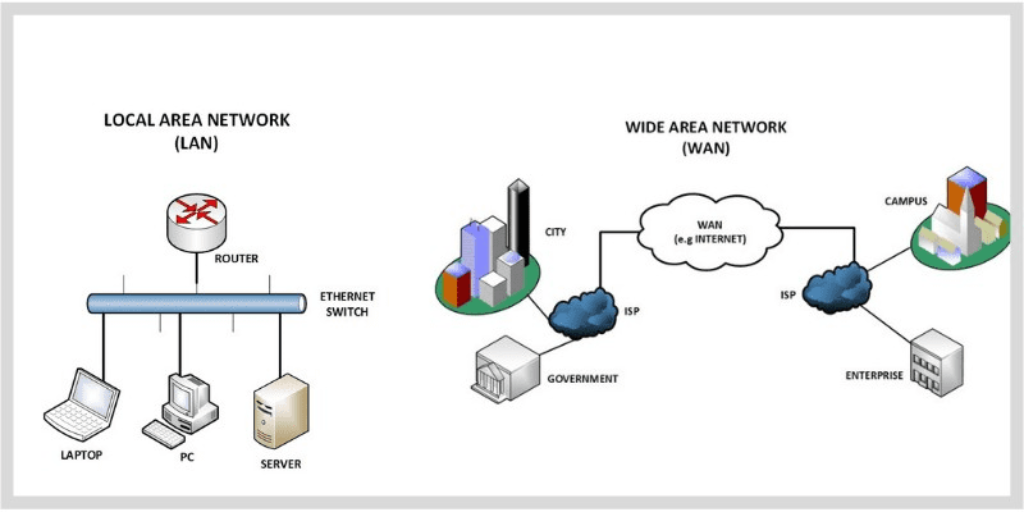
LAN, which stands for Local Area Network, is a network that connects devices within a limited geographical area such as a home, office building, or school. LANs are commonly used to facilitate communication and resource sharing among devices like computers, printers, and servers.
LANs are characterized by their high-speed connections and low latency, which make them ideal for transferring data quickly within a confined space.
A LAN is designed for private use, typically owned and managed by a single entity. It allows for seamless communication between connected devices, fostering collaboration and efficient data sharing. In a LAN environment, computers can easily communicate with each other, share files, access shared resources and even play multiplayer games.
LANs can be set up using wired or wireless connections, with Ethernet and Wi-Fi being the most common technologies employed.
LAN vs WAN: Which Is Better?
LAN vs WAN: Understanding the Differences
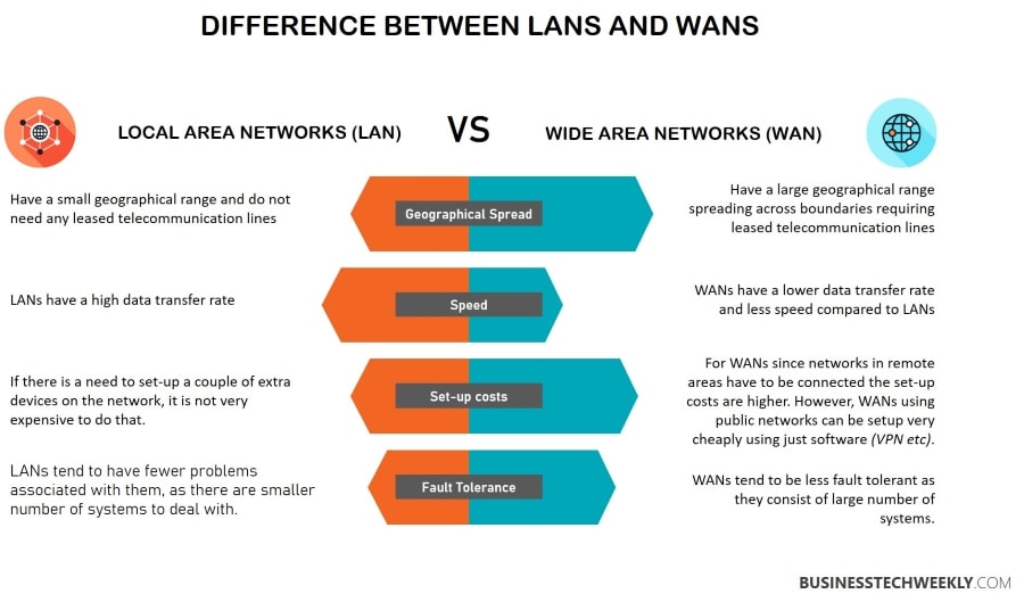
LAN vs WAN: the distinction between the two lies primarily in their geographic scope. While a LAN is limited to a small area, a WAN, or Wide Area Network, spans a larger geographical territory, connecting multiple LANs or other networks together. This distinction has significant implications for the design, performance, and accessibility of each network type.
WAN: Connecting the World
A WAN covers vast areas, often spanning cities, countries, or even continents. It facilitates long-distance communication and connectivity between disparate locations. Organizations with branches in different regions commonly use WANs to establish secure and reliable connections, enabling seamless data exchange and communication across distances.
Advantages
Some of the advantages of WANs include:
- Wide coverage area
- Scalability
- Multiple connectivity options
Disadvantages
Some of the disadvantages of WANs include:
- Slower speeds and limited bandwidth
- Less secure than LANs
- More complex to set up and maintain than LANs
- Higher cost than LANs
Unlike a LAN, a WAN is not limited to a single organization’s ownership. Instead, it is typically established and maintained by telecommunication companies or internet service providers. The Internet itself is the largest and most well-known example of a WAN, connecting billions of devices worldwide.
LAN: Powering Local Connectivity
In contrast, a LAN focuses on providing local connectivity within a confined area. LANs are primarily used to connect devices within a home, office, or educational institution.
Advantages
Some of the advantages of LANs include:
- Faster speeds and higher bandwidth
- More secure than WANs
- Easier to set up and maintain than WANs
- Lower cost than WANs
Disadvantages
Some of the disadvantages of LANs include:
- Limited coverage area
- Limited scalability
- Limited connectivity options
They enable users to share resources, such as printers and files, and facilitate smooth communication between connected devices. LANs offer high data transfer speeds, low latency, and a controlled environment, ensuring efficient and secure data transmission within a limited area.
LAN vs WAN: Use Cases
To better understand the practical applications of LANs and WANs, let’s explore some common use cases for each network type.
LAN Uses
- Home Networks: LANs are commonly employed in households to connect computers, smartphones, smart TVs, gaming consoles, and other devices for seamless communication and resource sharing.
- Office Networks: LANs provide the backbone for office networks, connecting computers, printers, servers, and other devices. They enable efficient data sharing, collaboration, and centralized management of resources.
- Educational Institutions: LANs are widely used in schools and universities to connect computers and facilitate e-learning, resource sharing, and communication among students and faculty members.
WAN Use Cases
Business Networks: WANs enable organizations to connect their branches and headquarters, ensuring secure data transfer, unified communication, and centralized management of resources and services.
Cloud Computing: WANs play a vital role in connecting users to cloud services, allowing them to access applications, storage, and computing resources hosted in remote data centers.
Video Conferencing: WANs are instrumental in supporting video conferencing platforms, enabling real-time communication and collaboration between individuals or teams located in different geographic locations.
LAN vs WAN: How to Set Up LAN and WAN?
Setting up a LAN typically involves the following steps:
- Choose the right equipment, such as routers, switches, and cables.
- Connect devices to the network.
- Configure the network settings.
- Test the network.
Setting up a WAN typically involves the following steps:
- Choose the right service provider.
- Determine the connectivity options, such as leased lines or VPNs.
- Configure the network settings.
- Test the network.
Conclusion
LAN vs WAN are both integral components of modern networking infrastructure, each serving a distinct purpose based on their geographical scope. LANs excel at providing high-speed connectivity and resource sharing within a limited area, while WANs facilitate long-distance communication and connect multiple LANs or networks together.
Understanding the differences between LAN vs WAN is crucial for designing and implementing efficient and secure network architectures. Whether you’re setting up a home network, establishing connectivity between office branches, or leveraging cloud services, comprehending the strengths and limitations of LANs and WANs will help you make informed decisions.
In summary, LANs are like local neighborhoods, fostering close-knit communication and efficient data sharing within a limited area, while WANs are the highways and bridges connecting these neighborhoods, enabling seamless communication and resource sharing across vast distances. So whether it’s LAN vs WAN, both have their unique roles to play in building a connected world.






